
The Houthi movement, known as Ansar Allah, is a Shia Islamist group that rose in Yemen during the 1990s. They are primarily Zaidi Shias, with leadership from the Houthi tribe. Initially opposing President Ali Abdullah Saleh, whom they accused of corruption and Western allegiance, the group gained prominence under Hussein al-Houthi. After Hussein’s death in 2004, the insurgency against Saleh began, and they’re now led by Hussein’s brother, Abdul-Malik al-Houthi.
Influenced by Hezbollah, the Houthis opposed U.S. and Israeli policies. They took part in the 2011 Yemeni Revolution and rejected the subsequent reconciliation, later seizing the capital with ex-President Saleh’s support. This action sparked the Saudi-led intervention and a protracted civil war, which has seen the Houthis launch attacks into Saudi Arabia and the UAE.
History of Houthi Movement

The Houthi movement in Yemen began as a moderate theological group called “the Believing Youth” (BY), advocating tolerance and founded in 1992 by Mohammed al-Houthi or his brother Hussein. Initially focusing on education through school clubs and summer camps, the BY aimed to revive Zaidi traditions in Saada, attracting thousands of students influenced by lectures from prominent Shia scholars.
According to Ahmed Addaghashi and Adam Baron, the movement grew as a response to foreign intervention and local grievances, such as Saudi ideological influence, Yemen’s alliance with the U.S., government corruption, and marginalization of Saada. Post the 2003 invasion of Iraq, the radicalization among some Zaidis increased, with anti-American and anti-Jewish sentiments becoming more pronounced, especially with followers of Hussein al-Houthi adopting such slogans.
Read Gabriel Attal Biography, Age, Education, Career and Net Worth
The radicalization and public dissent led to a crackdown in 2004, with mass arrests and a government operation to capture Hussein al-Houthi, who was killed later that year, sparking an insurgency. Despite the Yemeni and Saudi military efforts, the Houthis resisted effectively, even embarrassing the Saudis by withstanding their military might.
2011 Yemeni Revolution
The Houthis also engaged politically, participating in the 2011 Yemeni Revolution and the National Dialogue Conference but rejected the Gulf Cooperation Council deal, claiming it divided Yemen into rich and poor regions. They also suffered the assassination of their representative at the NDC.
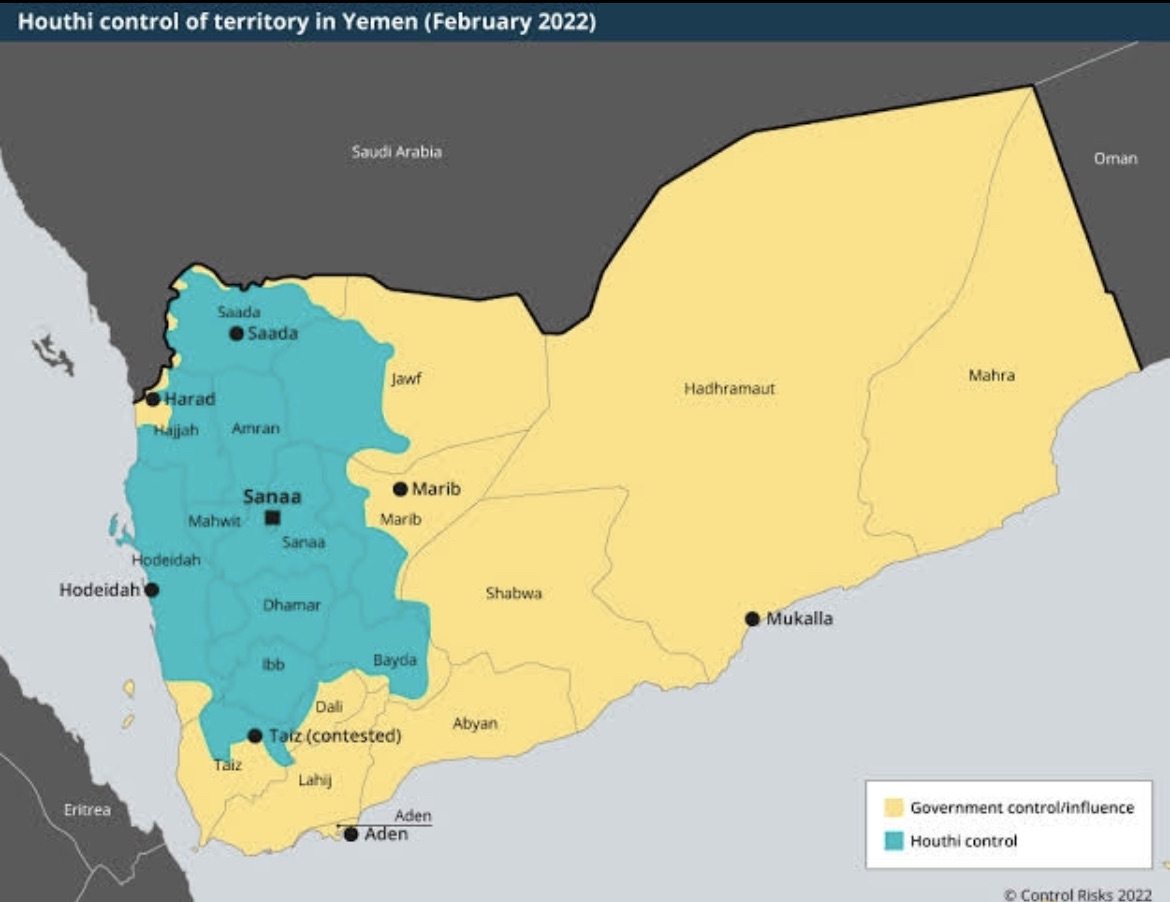
By 2012, the Houthis had expanded their control to several governorates, including access to the Red Sea and positioning themselves for further conflict, including possible moves against the capital, Sanaa. Their growth from a local movement to a significant force reveals the complex interplay of religion, politics, and regional dynamics in Yemen’s recent history.
By September 2014, Houthi rebels had taken control of parts of Sanaa, including government buildings. Their expansion was contested by Al-Qaeda and viewed with suspicion by Gulf States, who believed the Houthis received Iranian support while Saudi Arabia backed their Yemeni rivals.
In January 2015, the Houthis seized the presidential palace, and by February, they had dissolved parliament and declared their Revolutionary Committee as the acting authority. A deadly terrorist attack by the Islamic State against Houthi worshippers in March underscored the volatile situation.
Responding to Houthi advances, a coalition led by Saudi Arabia and supported by several countries, including the US, began airstrikes in Yemen in March 2015. By September, reports indicated that the Houthis, now known as Ansar Allah, had become a stable and organized movement, gaining popularity amid the power vacuum.
In late 2017, the alliance between former President Saleh and the Houthis disintegrated, leading to violent clashes and Saleh’s death at the hands of the Houthis in December.
The conflict has since spiraled into a complex humanitarian crisis. The United Nations describes the situation in Yemen as one of the world’s worst, with millions of people displaced and in dire need of humanitarian aid. The Houthis have been accused of obstructing aid deliveries and committing human rights abuses, while coalition airstrikes have been criticized for exacerbating civilian suffering.
Despite numerous attempts at peace talks and ceasefires, the conflict persists. The Houthis remain entrenched, benefiting from a sophisticated network of alliances and reportedly receiving support from Iran. Their drone and missile strikes into neighboring Saudi Arabia represent a persistent threat, underscoring the regional implications of the conflict.
The international community faces a conundrum in addressing the Houthi rebellion. There is a delicate balance between containing what some Gulf states see as Iranian expansionism and addressing the profound humanitarian needs of the Yemeni population. As the world grapples with these challenges, the Houthi rebels continue to hold significant sway, suggesting that any resolution to the Yemeni conflict must account for their role and influence. The road to peace will undoubtedly be long and fraught with complexity, but it is a necessary journey to end the suffering of millions.
Houthi Rebels – Israel Conflict

Amid the 2023 Israel-Hamas war, the Houthis expanded their operations to launch missiles at Israel and attack maritime interests in the Red Sea, claiming solidarity with Palestinians and the need to facilitate humanitarian aid to Gaza. An attempt to launch ballistic missiles at Israel was thwarted by Israel’s Arrow missile defense system, marking a notable engagement.
https://x.com/centcom/status/1745647248866738322?s=46&t=YbxKlCMxi6GrOhbYhGzFYQ
Is Houthis Rebels a Terrorist Organization ?

The US designated the Houthis as a terrorist organization in January 2021 but reversed this decision a month later under President Biden. In January 2022, Houthi missile and drone attacks targeted the UAE, marking a significant escalation with international implications.
